Effective Treatments for Gout: The Ultimate Guide
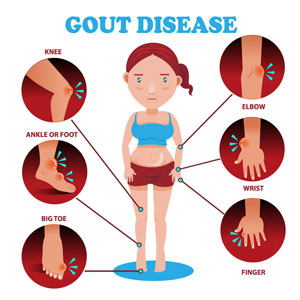
Gout is a type of arthritis characterized by sudden and severe pain, swelling, and redness in joints, often affecting the big toe. It occurs due to the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints and tissues, causing inflammation and intense discomfort. Managing gout involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes dietary adjustments. This guide explores the various treatment options available to effectively manage and prevent gout attacks. Zycolchin 0.5 Tablet is a medicine used to treat gout attacks and prevent gout recurrence in adults.
Understanding Gout:
Gout is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia. Uric acid forms crystals in joints and surrounding tissues, triggering painful gout attacks. Colchicine Over The Counter works by reducing the level of uric acid in the blood, which prevents the formation of hard uric acid crystals in the joints. Factors that can contribute to gout include:
- Dietary Choices: Consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol.
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase uric acid levels and contribute to gout.
- Genetics: Family history of gout can predispose individuals to developing the condition.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease can increase the risk of gout.
Treatments for Acute Gout Attacks:
During an acute gout attack, prompt treatment can help relieve pain and inflammation:
-
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen, naproxen, and indomethacin are commonly used to reduce pain and inflammation during gout attacks.
-
Colchicine: An anti-inflammatory medication that can reduce gout pain and inflammation. It is often prescribed at the onset of an attack and may cause gastrointestinal side effects.
-
Corticosteroids: Oral corticosteroids like prednisone or injections of corticosteroids directly into the affected joint can provide rapid relief from severe gout symptoms.
Long-Term Management and Prevention:
To prevent future gout attacks and manage the underlying causes of hyperuricemia, long-term management strategies are essential:
1. Medications to Lower Uric Acid Levels
-
Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors: Allopurinol and febuxostat are medications that lower uric acid production in the body. They are often prescribed for individuals with recurrent gout attacks or to maintain lower uric acid levels.
-
Uricosurics: Probenecid and lesinurad are medications that help the kidneys eliminate uric acid from the body. They are used in patients who overproduce uric acid or do not tolerate xanthine oxidase inhibitors.
-
Uric Acid Reducing Agents: Pegloticase is an enzyme that breaks down uric acid and is used for severe, refractory gout that does not respond to other treatments.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
-
Dietary Changes: Limit intake of purine-rich foods such as red meat, organ meats, shellfish, and alcohol (especially beer). Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy.
-
Weight Management: Losing excess weight can help reduce uric acid levels and decrease the frequency of gout attacks.
-
Hydration: Drink plenty of water and avoid sugary beverages to help flush uric acid from the body.
3. Avoid Triggers
-
Alcohol: Limit or avoid alcohol consumption, particularly beer and spirits high in purines.
-
Dehydration: Stay hydrated to prevent uric acid crystals from forming in the joints.
-
Medications: Discuss with your healthcare provider any medications that may increase uric acid levels or trigger gout attacks.
4. Natural Remedies and Supplements
While not substitutes for medical treatment, some natural remedies and supplements may help manage gout symptoms or support overall joint health:
-
Cherry Juice: Some studies suggest that cherry juice or cherries may help reduce gout attacks due to their anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Fish Oil: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil supplements may have anti-inflammatory effects and could potentially benefit individuals with gout.
-
Vitamin C: Some evidence suggests that vitamin C supplementation may lower uric acid levels and reduce the risk of gout attacks.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider if you experience recurring gout attacks or have difficulty managing symptoms despite lifestyle changes and medications. Untreated or poorly managed gout can lead to joint damage, kidney stones, and chronic arthritis.
Conclusion:
Managing gout involves a combination of acute attack treatment and long-term strategies to lower uric acid levels and prevent future flare-ups. By adopting lifestyle changes, taking prescribed medications, and avoiding triggers, individuals with gout can effectively control symptoms and improve their quality of life. Working closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan is essential for managing gout and minimizing its impact on daily activities. With proper management, many people with gout can achieve long-term relief and maintain joint health.